Atrial flutter is the second most common type of heart rhythm disorder after atrial fibrillation. The condition has no specific symptoms and is difficult to recognize until it becomes more severe.
1. What is atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter occurs when the atria of the heart begin to beat faster due to an excessive number of abnormal electrical impulses. The atria flutter as they attempt to contract, but this contraction occurs at a rate that is too fast. The atria can beat up to 300 times per minute, compared to the normal range of 60 to 100 times per minute.
2. Risk factors for atrial flutter
Atrial flutter is common in older adults. Generally, the rate of men having a higher risk of atrial flutter than women.
Factors that increase the risk of atrial flutter include:
- Age: Older adults have a higher risk than usual;
- Medical history: Individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease, heart valve problems, a history of myocardial infarction, and heart surgery;
- Hypertension: If not well-controlled, patients can have an increased risk of atrial flutter;
- Alcohol addiction;
- Family history of atrial flutter.
3. Causes of atrial flutter.
- Hypertension
- Myocardial infarction
- Heart valve abnormalities
- Congenital heart defects
- Hyperthyroidism
- After open-heart surgery
- After major non-cardiac surgery
- After congenital heart defect repair surgery
4. Symptoms of atrial flutter
5. Diagnosis of atrial flutter
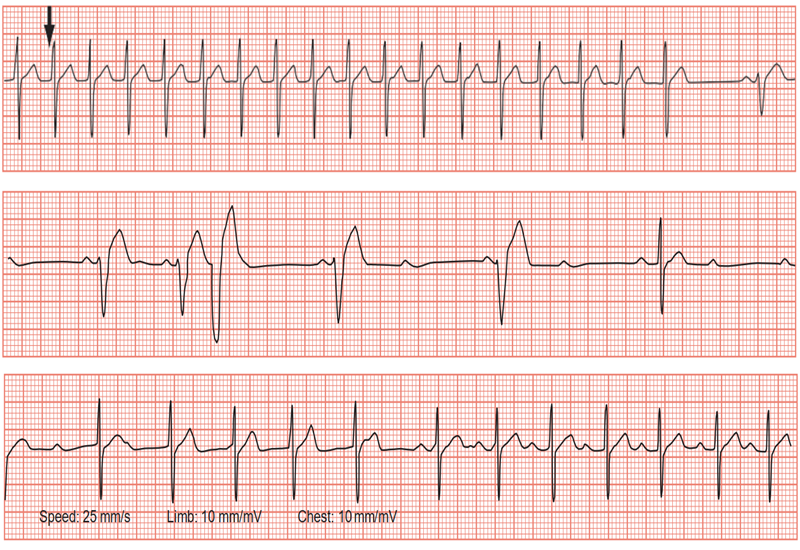
- Based on F waves on the ECG
- Regular sawtooth pattern
- Most evident in II, III, aVF
- F(+) in V1, V2
- F(-) in V5, V6
- Similar to solitary P waves in the precordial leads
- Counterclockwise atrial flutter F(-) in II, III, aVF, V6 and F(+) in V1
- Clockwise atrial flutter F(+) in II, III, aVF, and often has a notch.
6. Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
7. Preventive Measures for Atrial Fibrillation
- Follow up as scheduled for monitoring the progression of the disease and your health status.
- Follow the doctor’s instructions; do not take medications not prescribed or skip medications from the prescription provided to you.
- Quit smoking.
- Limit the use of alcoholic substances
- Consume heart-healthy foods, minimize fat intake
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Reduce stress