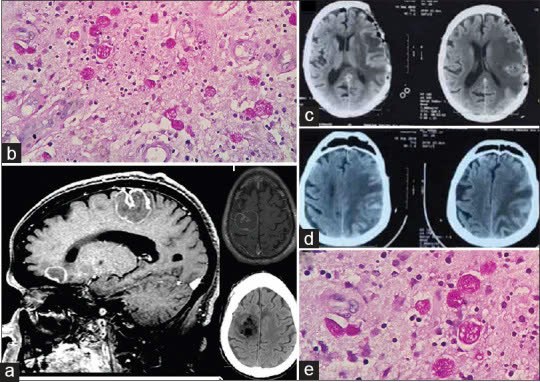
Amoebic brain abscess is a common condition in tropical regions, with highly diverse clinical manifestations. Early detection and treatment are crucial for patient survival. Late diagnosis often leads to severe complications, permanent neurological damage, and a high mortality rate.
Treatment Methods for Amoebic Brain Abscess
Treatment involves both medical and surgical approaches. Outcomes depend on several factors:
-
The patient’s overall health
-
Disease progression and diagnostic timing
-
Size, number, and location of abscesses
-
The extent of brain damage
Early intervention is essential to minimize complications. Current treatment strategies include:
-
Amoebicidal drugs
-
Drainage of pus (if abscesses have formed)
-
Combination antibiotic therapy
-
Surgery combined with amoebicidal medication
To date, no universally optimal treatment protocol exists. Due to rapid disease progression and frequent misdiagnosis (often confused with bacterial meningitis), many cases receive incorrect initial treatment. Consequently, mortality rates remain high, and survivors often suffer lasting neurological deficits.
In reality, very few patients with cerebral amoebiasis achieve full recovery. Nevertheless, early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve survival chances.
Medications Used in Treatment
Theoretically, treatment requires amoebicidal drugs (monotherapy or combination therapy) that effectively cross the blood-brain barrier. The U.S. CDC recommends:
1. Amphotericin B
-
An antifungal administered intravenously or intrathecally to kill amoebae.
-
Proven effective in trials but shows cautious clinical prognosis.
2. Rifampin
-
Intravenous use demonstrates efficacy in studies, but real-world outcomes for brain-invading amoebae remain uncertain.
3. Fluconazole
-
Intravenous administration is indicated for amoebic brain abscess.
4. Combination Therapy
-
Research explores Amphotericin B + Rifampin or Fluconazole, but survival rates in small-scale studies are inconsistent. Further evaluation is needed.
5. Azithromycin
-
Shows high efficacy in animal models and may synergize with Amphotericin B.
Surgical Indications
Surgery is required when:
-
Abscesses are drug-resistant
-
Gas-forming abscesses are present
-
There is a risk of rupture
-
Intracranial pressure increases dangerously
Prevention of Amoebic Infection
Amoebic brain abscess is life-threatening, and survivors often face long-term disabilities. Thus, prevention is paramount. Simple hygiene measures can significantly reduce risk:
-
Handwashing with soap or disinfectant before eating.
-
Avoiding contamination of food/water by amoebic cysts, especially in rural areas.
-
Safe farming practices:
-
Never use untreated human waste as fertilizer.
-
Prevent fecal contamination of water sources.
-
-
Food safety:
-
Avoid raw foods (e.g., salads, ceviche).
-
Wash vegetables thoroughly; use UV-treated water to kill cysts.
-
-
Treat cyst carriers with metronidazole to eliminate infection.
Conclusion
Amoebic brain abscess demands urgent, aggressive treatment. While drug therapy and surgery can save lives, prevention through hygiene remains the most effective strategy. Early medical intervention is critical to improving survival and reducing neurological sequelae.