Bleeding gums is a symptom of one of several conditions such as periodontitis, gingivitis, etc. So what should one do when experiencing gum bleeding?
1. What is bleeding gums?
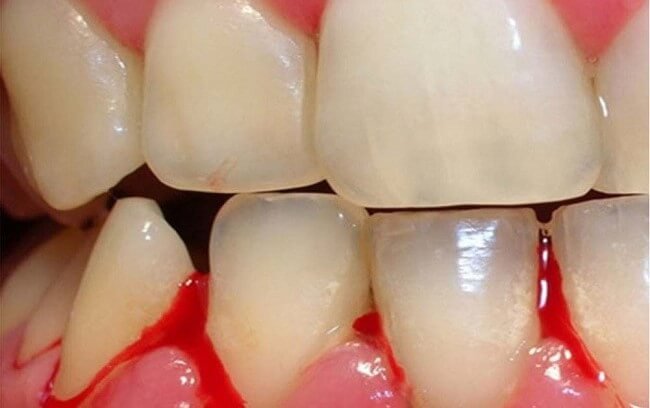
Bleeding gums is the condition of bleeding in the area of the gums, often occurring when brushing teeth. In addition to bleeding, patients may also experience symptoms such as bad breath, swollen gums, etc.
2. Why do gums bleed?
Bleeding gums can be a symptom of various dental conditions such as periodontitis, gingivitis, or other health issues.
- Periodontitis: Teeth are supported and held in the jawbone by the surrounding tissue known as the periodontium. Periodontitis often progresses silently and is the cause of loose teeth and even tooth loss. The typical symptom of this condition is bleeding at the gum line due to tartar buildup around the teeth, causing inflammation.
- Gingivitis: Teeth are protected and securely held by the gums. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene, allowing tartar and plaque to form and lead to inflammation. The typical symptoms of this condition also include bleeding at the gum line, swollen gums, red gums, and bad breath.
- Dental abscess: Untreated dental infections, broken teeth, or perforations allow bacteria to invade and attack the gums, leading to an abscess. The typical symptom of a dental abscess is also bleeding gums. When the patient experiences continuous gum pain, generalized fever, and facial swelling, it may indicate a severe case of dental abscess.
- Vitamin deficiency, malnutrition: The body being malnourished or lacking in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C and K can also be a cause of bleeding at the gum line. In addition to this symptom, the patient may also experience bone pain, drowsiness, and difficulty breathing (due to vitamin C deficiency).
- Use of anticoagulant medication: Anticoagulant medications prescribed to some patients to reduce blood clotting can cause bleeding at the gums.
- Hormonal changes: In females, when the body enters puberty, pregnancy, menopause, or when using birth control pills, hormonal changes can lead to bleeding at the gums.
- Dengue fever: When suffering from dengue fever, especially in severe stages, the disease can cause symptoms such as bleeding in the skin, gums, nosebleeds, and even gastrointestinal or cerebral hemorrhaging, which can threaten the patient’s life.
- Oral cancer: This disease can cause symptoms such as bleeding gums, bad breath, difficulty chewing or swallowing, swelling or lymph node enlargement, and ulcers in the oral cavity.
- Other diseases: Anemia, infections, breast cancer, and other conditions can also cause bleeding in the gums.
3. What to do if you have bleeding gums?
- Brushing teeth twice a day (in the morning upon waking and at night before going to bed) and after each meal (10 minutes after eating).
- Brushing correctly, using dental floss, and a soft toothbrush for oral hygiene.
- Not smoking, eating a balanced diet, and particularly ensuring adequate vitamin C intake to prevent bleeding gums due to vitamin C deficiency.
- Regular dental check-ups, scaling every six months to prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can cause gum inflammation and other oral health issues.