Mammography is a non-invasive technique that is widely used in diagnosing breast disorders. Mammography with contrast agent helps display clearer images, assisting doctors in making accurate diagnoses. So, when is this technique indicated, and what are its advantages and limitations?
Ductal imaging is a method of mammography that involves injecting a contrast agent to visualize the breast ducts. This technique is primarily used in cases where female patients have clear discharge or bleeding from the nipple but have normal mammography results (non-contrast mammography). It is important that before performing this technique, patients should not squeeze the nipple as a small amount of fluid in the duct can aid in diagnosing breast disorders.
1. What is ductal imaging (galactography or ductography)?
Ductal imaging is a technique that uses a low-dose X-ray system combined with the injection of a contrast agent through the duct of the nipple to investigate the breast ducts. It is important to understand that:
Mammography is a non-invasive technique that uses X-rays to examine breast images, assisting doctors in diagnosing breast diseases. It is the oldest and most frequently used medical technique.
The breast mainly consists of three main structures: fatty tissue, lobules (which produce milk), and milk ducts (which carry milk from the lobules to the nipple). Plain mammography, without the use of contrast agents, also known as a mammogram; ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast are the primary methods for breast imaging. However, to clearly assess the milk ducts, mammography combined with the injection of a contrast agent into the milk ducts around the nipple is needed.
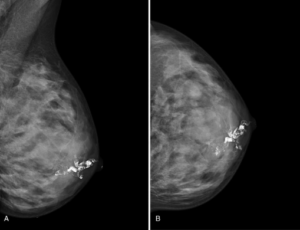
2. When is this technique used?
Ductal imaging (galactography or ductography) is most commonly used in cases where female patients have clear discharge or bleeding from the nipple, and no pathology is found through plain mammography (without contrast).
Ductal imaging should not be performed in the following cases:
- Discharge from the nipple that is cloudy white, blue, green, or gray is usually not a cause for concern.
- Discharge from both breasts in women who have not given birth may simply be a side effect of medication or may be related to a pituitary gland issue in the brain, making ductal imaging unnecessary.
3. What to prepare before having a mammary duct imaging
- The only requirement is that you should not squeeze the nipple before performing the technique, as in some cases, a small amount of fluid in the milk ducts can determine the cause of the disease.
- You should inform your doctor about any medications being used, any history of allergies (if any), especially a history of allergy to contrast agents. Additionally, you need to inform your doctor about any medical conditions you have had or are currently experiencing.
- Always inform your doctor or radiologic technician about whether you are pregnant.
- Do not use deodorant, powder, or lotion under your arms and on your chest on the day of the procedure. This is simply because these substances can affect the quality of the diagnosis.
- Furthermore, before the examination, you should leave all jewelry at home. You will need to change into a hospital gown when undergoing this procedure.
4. How does the mammary duct imaging technique detect abnormalities?
5. How is this technique performed?
6. What will I experience during and after the ductal imaging?
7. What are the benefits and risks of ductal imaging?
7.1 Benefits
- Ductal imaging can detect benign or malignant tumors, aiding in early and timely diagnosis and treatment.
- This technique helps locate tumors, guiding the surgeon.
- Low-dose X-rays typically have no side effects in this procedure.
7.2 Risks
- There is always a small risk of cancer due to excessive exposure to X-ray radiation. However, in this technique, the benefits for early diagnosis and treatment far outweigh the risks.
- Damage to the milk ducts can occur during catheter placement or when injecting contrast material. This is not dangerous as most injuries will heal on their own after a short time.
- There is a possibility of breast infection or mastitis, but it is not common.

