Both women and men are concerned about the signs and symptoms of breast cancer. However, breast cancer does not always present clearly clinically, especially in the early stages. Therefore, a breast cancer screening plan using various methods such as mammography needs to be widely implemented.
1. Unusual nipple discharge
In pregnant or breastfeeding women, discharge from one or both breasts is usually milk. However, when not in these circumstances, nipple discharge can be seen as an early sign of breast cancer.
It is quite common for many women to visit the doctor due to unusual white discharge from both nipples. Subsequently, some tests will be ordered, and the results may raise suspicion of cancer. Mammography detects small lumps scattered throughout the breast tissue. These women are often recommended for breast removal surgery. Pathological anatomy evaluates the histopathology of the tumor, allowing for a definitive diagnosis, with results often indicating ductal carcinoma in situ, an early form of breast cancer.
However, abnormal nipple discharge is not always a sign of malignant pathology. A study conducted on hundreds of women concluded that nipple discharge does not have a strong correlation with breast cancer. This symptom can also occur in other conditions such as galactorrhea syndrome or milk ejection syndrome. The first thing to do when noticing abnormal nipple discharge is to see a doctor, rather than panic.
2. Nipple bleeding
Most women feel scared of having breast cancer if they notice blood coming from the nipple. This can be a symptom of breast cancer; however, it is mostly related to other benign conditions and is not harmful. Causes of nipple bleeding include:
- Papilloma of the mammary duct, an abnormal proliferation inside the duct but lacking malignant characteristics.
- Dilation of the mammary duct due to the duct’s lumen being enlarged and the duct wall thickening.
- Trauma: Rough clothing material rubbing against the breast, especially during physical activity.
If the exact cause of nipple bleeding is unknown, the patient should see a doctor immediately for consultation and examination to identify any underlying pathology if present.
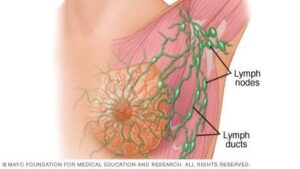
3. Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are a component of the immune system, containing lymphocytes that protect the body by detecting and destroying pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Swollen lymph nodes are also a sign of breast cancer, although the occurrence rate is not high. Breast cancer often causes swelling in the axillary or supraclavicular lymph nodes. Typically, patients do not pay attention to this symptom until the tumor appears and increases in size. Therefore, whenever one feels swelling in the lymph nodes in the axillary area and around the collarbone, they should not be complacent and should immediately seek medical facilities for timely diagnosis and detection.
4. Itchy nipple
Itchy nipples are a common clinical symptom, often self-limiting or responding well to regular anti-itch creams. However, itchy nipples can also be a manifestation of other medical conditions, including Paget’s disease. This is a rare form of breast cancer occurring at the nipple, which then spreads to surrounding tissues. In this situation, itchy nipples are considered an early symptom of breast cancer. Patients may also exhibit other external symptoms such as:
- Redness and swelling of the nipple
- Nipple sensitivity
- Thickened breast skin
- Inverted nipple
- Abnormal nipple discharge, which may be accompanied by blood.
The symptoms of Paget’s disease are easily confused with local skin conditions such as dermatitis or eczema. If the itching does not subside, the patient should see a doctor for examination and guidance on monitoring the progression of the disease. Surgery is the main treatment method if Paget’s disease is diagnosed.
5. Breast swelling and pain
Breast swelling and pain can result from various causes, with infection being the most common. Additionally, breast swelling and pain can be a sign of inflammatory breast cancer. This is a rare form of breast cancer that typically does not form a breast tumor. Instead, the patient’s breast will undergo several changes and quickly become:
- Enlarged breast, with a noticeable increase in size
- Change in breast skin color to red or purple
- Warm swelling of the breast
- Orange peel appearance of the breast skin
- Swelling and pain
In inflammatory breast cancer, malignant cells block the lymphatic ducts in the area, causing fluid accumulation and leading to the clinical symptoms mentioned above.
Doctors have always recommended that women perform monthly breast self-exams at home. The purpose of this measure is to detect suspicious lumps at an early stage, although recent studies suggest that most histological results from tumors detected this way are not malignant. Nowadays, experts agree that women need to raise their awareness about their breast health rather than simply performing self-exams. Each woman should pay attention to the shape, color, size, and tissue characteristics. Any abnormalities related to these features should be addressed and clarified by consulting specialists.