The breast is composed of connective tissue, glandular tissue, and fatty tissue. Your breast is considered dense when you have a lot of connective and glandular tissue with little fatty tissue. Breast tissue density can decrease with age but often varies and changes among different women.
1. How can you know if you have dense breast tissue?
Breast tissue density is determined by radiologists – the doctors who read mammograms. There are 4 types of breast tissue density, and doctors will determine which type each woman’s mammogram falls into based on measurement scales. When you go for a mammogram, ask your doctor or check the results to find out your breast density type.
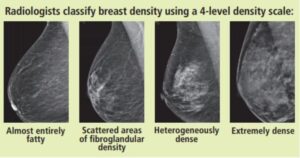
Breast tissue density in the U.S.:
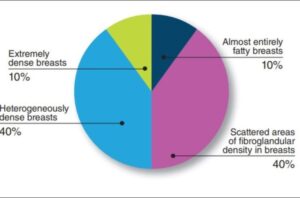
- 10% of women have almost all fatty tissue
- 10% of women have almost all glandular tissue
- 80% of women have a density that is intermediate between fatty and glandular tissue
In Vietnam, the proportion of women with dense breasts is often higher due to smaller body size and lower obesity rates, so typically a combination of mammography and breast ultrasound will increase the accuracy in early-stage breast cancer screening. Some factors associated with increased breast tissue density include having children later, not breastfeeding, and using hormone therapy in the past.
2. Why is breast tissue density important?
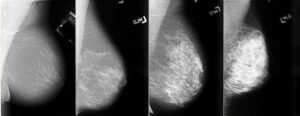
If you have dense breast tissue, it increases the risk of breast cancer (by 4 to 6 times), and dense breasts also make it more difficult for doctors to detect breast cancer on mammograms. Dense breasts will appear white on mammograms, and both benign and malignant tumors also appear white. Therefore, mammograms may be less accurate in women with dense breasts.
3. If I have dense breasts, do I need a mammogram?
Mammography is the only medical method recognized by the FDA as a screening method that reduces the mortality rate from breast cancer. Many breast cancers are detected on mammograms even if you have dense breasts.
4. Are there any breast cancer screening methods better than mammography for dense breasts?
In cases of dense breast tissue, cancer may be difficult to detect on 2D mammograms. 3D mammography provides images of the breast tissue in slices from different angles, making it easier to assess abnormalities. 3D mammography increases the number of cancer detections without requiring additional methods. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also help find additional cancers that may not be visible on mammograms. However, both MRI and ultrasound can detect many non-cancerous lesions.
5. If I have dense or non-dense breast tissue, what should I do?
If you have dense breast tissue, talk to your doctor to discuss which screening methods are appropriate and what additional methods may be needed for screening.
If your breasts are not dense, other factors may affect your risk of developing breast cancer, including family history, previous chest radiation, and prior breast tissue biopsies, which can increase the risk of breast cancer. Discuss your history with your doctor.
Even if you do not have a family history and have fatty breast density, you still need to have a mammogram once a year starting at age 40.