Dense breast tissue is a common condition with certain points to consider. Below are some frequently asked questions about breast density.
1. What is dense breast tissue??
The structure of the breast consists of various components (glandular tissue, connective tissue, and fatty tissue). The density of breast tissue is a term used to describe the ratio of glandular tissue to the overall breast tissue in mammogram results. Dense breast tissue is when there is a significant amount of glandular and connective tissue, while the amount of fatty tissue in the breast is relatively low.
2. How to determine if you have dense breast tissue or not?
Dense breast tissue cannot be determined through breast self-exams or clinical breast exams; it can only be assessed based on mammogram results that indicate whether the breast tissue is dense or not.
3. Is dense breast tissue common?
About half of mammogram results for women aged 40 and older show dense breast tissue. The density of breast tissue is often natural, but there are other factors that can influence it.
Factors associated with lower breast density include older age, having children, and using tamoxifen. Factors associated with dense breast tissue include using hormone replacement therapy after menopause and having a low body mass index (BMI).
4. How is breast density classified based on mammogram results?
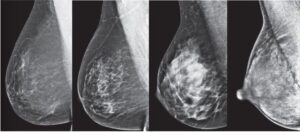
The classification of breast tissue density is currently used by doctors according to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS). This classification system was developed by the American College of Radiology, and the classification results are indicated by letters, specifically:
- A: The breast composition is mostly fatty tissue (about 10% of women).
- B: Scattered areas of fibroglandular tissue, but the main breast composition is still fatty tissue (about 40% of women).
- C: Heterogeneously dense breast tissue, meaning there are still areas of fatty tissue, but the main breast composition is dense tissue (about 40% of women).
- D: Extremely dense breast tissue (about 10% of women).
If the breast density is A or B, it means the breast has low fibroglandular density or is predominantly fatty. If the breast density is C or D, it means the breast has dense tissue or is considered dense.
5. How does having dense breast tissue affect mammography for women?
On mammogram results, dense breast tissue appears white, similar to abnormal changes (such as tumors), making the interpretation of mammogram results more challenging, as signs of breast cancer may be obscured and go undetected. Women with dense breast tissue will need to combine additional techniques to enhance the detection of breast cancer. Ultrasound is the most common choice. In addition to ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging is also a very valuable screening method.
6. Is dense breast tissue a risk factor for breast cancer?
Dense breast tissue is a risk factor for breast cancer; women with dense breasts face a higher risk of developing breast cancer compared to women with more fatty breasts.
Dense breast tissue not only increases the risk of breast cancer but also complicates the interpretation of mammogram results.
7. Do women with dense breast tissue need additional breast cancer screening methods beyond mammography
The answer is yes: According to the latest recommendations from the American Cancer Society regarding breast cancer screening, in addition to mammography, other supplemental screening techniques (such as ultrasound or breast MRI) performed on women with dense breast tissue will help increase the likelihood of detecting breast cancers.

