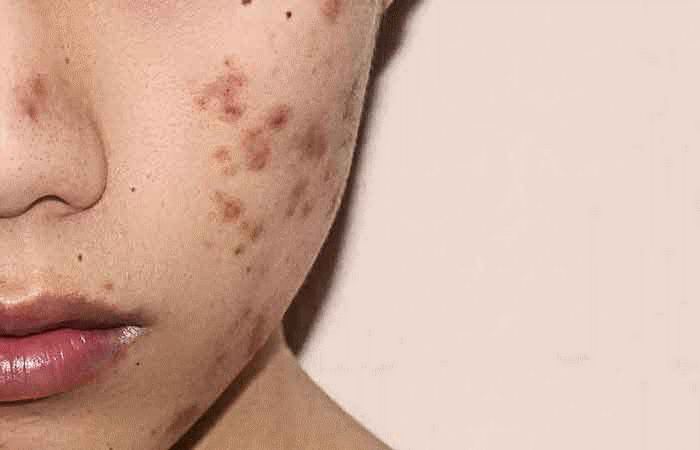
Skin pigmentation will result in dark spots or patches on the face, arms, and areas of the body that are directly exposed to sunlight. This condition is usually not harmful, but it affects the aesthetics and quality of life of those with this skin.
1. What is skin pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation is a term used to describe skin that has changed color and is darker than normal. It can occur in small patches. However, this condition can appear in larger areas affecting the entire body.
Is skin pigmentation dangerous? Experts have indicated that although skin pigmentation is usually not harmful, it may be a symptom of another underlying condition. Therefore, it is important to thoroughly investigate the types of pigmentation, their causes, and how to treat them.
2. Types of skin pigmentation
There are several types of skin pigmentation, among which the most common are melasma, dark spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Melasma: This condition is believed to be caused by hormonal changes and can develop during pregnancy. The pigmented areas can appear on any part of the body, but they are most commonly seen on the abdomen and face.
- Dark spots: This condition is also referred to as liver spots or solar lentigines. It appears as dark spots that are common. This condition is related to excessive sun exposure over extended periods. Generally, they appear as spots in areas exposed to sunlight.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: This is the result of trauma or dermatitis. A common cause of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is acne.

3. Symptoms of hyperpigmentation and some risk factors
Dark areas appearing on the skin are the main symptoms of hyperpigmentation. The dark patches can vary in size and can develop on any part of the body. The greatest risk factors for hyperpigmentation symptoms in general are due to sun exposure and dermatitis. Both of these factors can increase the production of the pigment melanin. The more exposure you have to sunlight, the higher the risk of skin hyperpigmentation.
However, it also depends on the disorder along with other risk factors for the hyperpigmented patch, which may be due to the use of contraceptives. In this case, the skin may experience pigmentation, becoming darker and more susceptible to changes in pigmentation. Or medications that increase the body’s sensitivity to sunlight. Or trauma on/in the skin, such as wounds or burns on the surface of the skin.
4. Causes of hyperpigmentation
One of the common causes of skin hyperpigmentation is the overproduction of melanin. Melanin is a pigment that gives skin its color. It is produced by skin cells called melanocytes. Various conditions or factors can alter melanin production in the body, leading to pigmentation disorders.
- Some types of medications can cause hyperpigmentation: Additionally, some chemotherapy drugs used during treatment may be responsible for hyperpigmentation due to their side effects.
- Pregnancy alters hormone levels in the body, and it can also influence melanin production in some women.
- A rare endocrine disease such as Addison’s disease: This condition can cause the most noticeable hyperpigmentation in areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands, or in areas subject to friction, like the elbows and knees.
Skin hyperpigmentation is a direct result of increased hormone levels in the body leading to increased melanin pigment synthesis. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to sunlight is also a cause of increased melanin.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of hyperpigmentation
Dermatologists can diagnose the cause of skin hyperpigmentation; they will inquire about the history and medical background of the hyperpigmentation condition, and the doctor will conduct a physical examination to determine a clearer cause. In cases where no cause and typical symptoms are found, the doctor may use a skin biopsy method to narrow down the underlying cause, aiding in a more accurate diagnostic process.
Treatment of hyperpigmentation can utilize several types of prescription medications from a doctor. This medication often contains hydroquinone, which acts to lighten the skin. However, using topical hydroquinone for a prolonged period (without any breaks during use) can cause skin darkening, also known as dermatitis. Therefore, it is best to use topical hydroquinone only under the guidance and prescription of a dermatologist to ensure no side effects affect skin health.
Additionally, topical retinoids can be used to help brighten dark spots on the skin. Both types of medications must be used for an extended period of a few months to effectively lighten areas of skin with hyperpigmentation. A doctor may also recommend laser treatment or chemical peels to reduce hyperpigmentation, including melasma. However, the suitability of these treatments will depend on the underlying cause of the skin’s hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation can be managed at home with over-the-counter medications that can lighten dark spots. These products do not contain as much hydroquinone as dermatologist-prescribed medications. Furthermore, it is essential to use sunscreen for the skin, as sunscreen is the most crucial factor in improving most causes of pigmentation.
Some sunscreen standards selected for hyperpigmented skin include:
- Physical sunscreen is the best choice, as its ingredients contain zinc oxide.
- Sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 is recommended, with coverage extending to 50.
Use sunscreen daily and reapply every 2 hours to enhance skin protection effectiveness. Hyperpigmentation may also result from skin disorders related to sunlight, such as melasma. Therefore, it is a factor that can play an important role in increasing skin pigmentation. In this case, use a mineral sunscreen containing iron oxide in its ingredients, as it can block some sunlight. Additionally, wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
6. Measures to Prevent Hyperpigmentation
It is not always possible to prevent skin hyperpigmentation. However, certain measures can help reduce the risk factors contributing to pigmentation:
- Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, particularly prioritizing physical sunscreen products.
- Wear hats and long clothing to block sunlight.
- Avoid sun exposure during peak intensity times of the day, typically from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Avoid certain medications that may pose a risk of hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation is generally not harmful, and it often indicates a few serious medical conditions. In some cases, dark areas may fade with good sun protection. In other instances, active treatment is necessary. There is no guarantee that dark spots will completely fade, even with treatment.